
During manufacturing processes, a mold has the most critical importance in achieving high-quality components which are high precision. Thus for a mold to be dependable and able to perform for long, there should be meticulous care, stringent quality standards and application of certain modern practices. This article seeks to look at how one can maintain, or guarantee the quality of a manufactured mold and will provide some practical guidance to those looking to upgrade their manufacturing strategies.
1. Material selection
This is the first and crucial step in determining the quality of the mold: the selection of the proper material. Dependable materials such as hardened steel or aluminum or tough metals should be sourced as per the application. For instance, in the case of injection molds, heat, and pressure withstanding materials are needed. If some of the components are made from cheap materials, damage is bound to occur prematurely, the lifecycle of the mold performance decreases and the production costs rise.
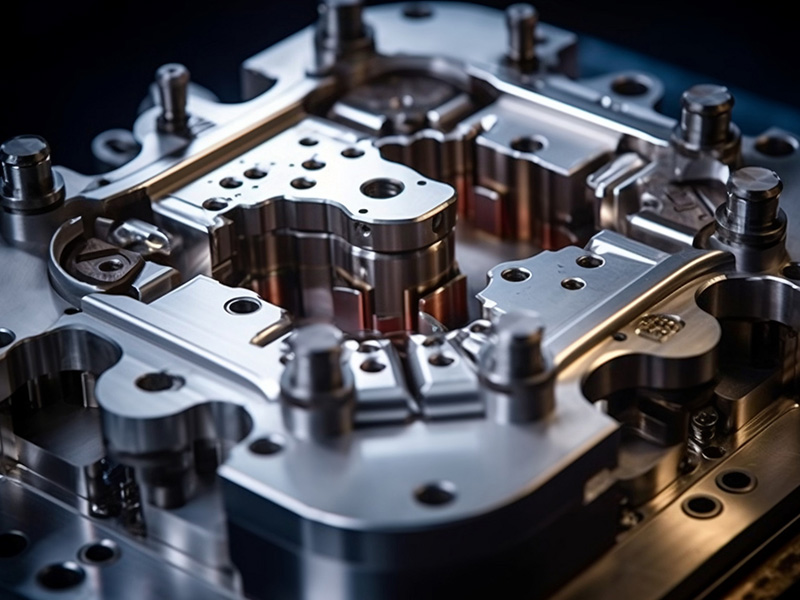
2. Precision Design And Engineering
A well-done mold can only be made using precision engineering design and drafting processes. Mold designs have to be architected using computer-aided design (CAD) programs by the engineers. Even before the mold is constructed, more advanced simulations can be used to predict potential problems such as those relating to the flow of the material or rates of cooling.
3. Manufacturing Process Control
Once the designer comes up with a final design of the mold, it is very necessary to control the process of fabrication closely. For that, the CAD models can be faithfully reproduced during the mold making process thanks to CAM technologies, CNC Machining and electrical discharge machining (EDM). Improvements of the monitoring strategy include continuous adjustments of the machining operation to avoid any concerns that can cause variations from the design of the mold which may endanger its quality.
4. Dimensional Accuracy Testing
Dimensional measures accuracy is one of the features considered in the mold manufacture where any out of the ordinary will affect the end product. To avoid dealing with inaccurate dimensions, manufacturers have sophisticated measuring devices which include CMM. These machines protect the information molded in so as to maintain uniformity of production even if several parts are made at a given time.
5. surface finish Quality
Surface finish quality of a mold determines the appearance and usability of the final product. Inappropriate surface finish can cause certain defects such as rough surfaces or poor product release. There are manufacturers who are able to properly polish and finish edges, as well as provide special tools to attain the necessary smoothness.
6. Heat Treatment
Heat treatment is extremely important for increasing the strength and durability of molds. If molds are treated properly, they will last a longer time to avoid fractures and generate thousands of parts with no deterioration in the long run. Increasing the life and performance of molds can be achieved by subjecting them to processes like tempering and hardening.
7. Mold Testing and Trial Runs
Prior to mass production of a mold, testing and trial runs are necessary. In this stage, some preliminary conclusions are made regarding potential pitfalls in molding performance such as parameters of the part accuracy, its location, and its operational capability. In course of the mentioned empirical research, alterations are made by the manufacturers to ensure that the mold is made to work effectively in real situations.
8. Sustaining the Status Quo
Additionally, even though the manufacture may have passed the first test, the quality of the tool should be maintained routinely. After every production run the tool should be cleaned, lubricated, and checked for damage in order to reduce wear. This ensures that the tool remains effective over a long period of time and reduces the necessity of timely replacement.
Among other factors discussed above as regards why some firms procure molds only that fails to ensure that the quality of the manufactured molds includes the right type of materials, design, control of production operations, and mold testing possibilities. If producers build around these critical bases, they will optimize production by meeting never before seen consistency and quality in finished molds thereby ensuring that end-users are megas pleased.